It is New Year's Day and people are in line for the Wonderland rollercoaster ride. Each person wears a sticker indicating their initial position in the queue from to . Any person can bribe the person directly in front of them to swap positions, but they still wear their original sticker. One person can bribe at most two others.
Determine the minimum number of bribes that took place to get to a given queue order. Print the number of bribes, or, if anyone has bribed more than two people, print Too chaotic.
Example
If person bribes person , the queue will look like this: . Only bribe is required. Print 1.
Person had to bribe people to get to the current position. Print Too chaotic.
Function Description
Complete the function minimumBribes in the editor below.
minimumBribes has the following parameter(s):
- int q[n]: the positions of the people after all bribes
Returns
- No value is returned. Print the minimum number of bribes necessary or
Too chaoticif someone has bribed more than people.
Input Format
The first line contains an integer , the number of test cases.
Each of the next pairs of lines are as follows:
- The first line contains an integer , the number of people in the queue
- The second line has space-separated integers describing the final state of the queue.
Constraints
Subtasks
For score
For score
Sample Input
STDIN Function
----- --------
2 t = 2
5 n = 5
2 1 5 3 4 q = [2, 1, 5, 3, 4]
5 n = 5
2 5 1 3 4 q = [2, 5, 1, 3, 4]
Sample Output
3
Too chaotic
Explanation
Test Case 1
The initial state:
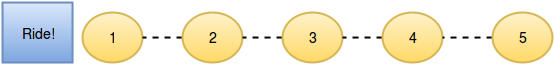
After person moves one position ahead by bribing person :
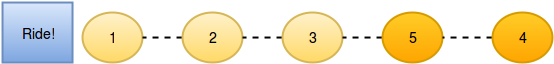
Now person moves another position ahead by bribing person :
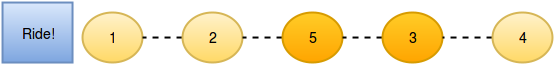
And person moves one position ahead by bribing person :
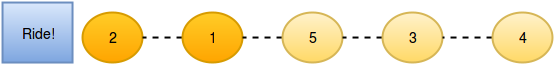
So the final state is after three bribing operations.
Test Case 2
No person can bribe more than two people, yet it appears person has done so. It is not possible to achieve the input state.