Determine the minimum cost to provide library access to all citizens of HackerLand. There are cities numbered from to . Currently there are no libraries and the cities are not connected. Bidirectional roads may be built between any city pair listed in . A citizen has access to a library if:
- Their city contains a library.
- They can travel by road from their city to a city containing a library.
Example
The following figure is a sample map of HackerLand where the dotted lines denote possible roads:
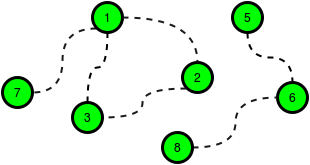
The cost of building any road is , and the cost to build a library in any city is . Build roads at a cost of and libraries for a cost of . One of the available roads in the cycle is not necessary.
There are queries, where each query consists of a map of HackerLand and value of and . For each query, find the minimum cost to make libraries accessible to all the citizens.
Function Description
Complete the function roadsAndLibraries in the editor below.
roadsAndLibraries has the following parameters:
- int n: integer, the number of cities
- int c_lib: integer, the cost to build a library
- int c_road: integer, the cost to repair a road
- int cities[m][2]: each contains two integers that represent cities that can be connected by a new road
Returns
- int: the minimal cost
Input Format
The first line contains a single integer , that denotes the number of queries.
The subsequent lines describe each query in the following format:
- The first line contains four space-separated integers that describe the respective values of , , and , the number of cities, number of roads, cost of a library and cost of a road.
- Each of the next lines contains two space-separated integers, and , that describe a bidirectional road that can be built to connect cities and .
Constraints
- Each road connects two distinct cities.
Sample Input
STDIN Function
----- --------
2 q = 2
3 3 2 1 n = 3, cities[] size m = 3, c_lib = 2, c_road = 1
1 2 cities = [[1, 2], [3, 1], [2, 3]]
3 1
2 3
6 6 2 5 n = 6, cities[] size m = 6, c_lib = 2, c_road = 5
1 3 cities = [[1, 3], [3, 4],...]
3 4
2 4
1 2
2 3
5 6
Sample Output
4
12
Explanation
Perform the following queries:
HackerLand contains cities and can be connected by bidirectional roads. The price of building a library is and the price for repairing a road is .

The cheapest way to make libraries accessible to all is to:
- Build a library in city at a cost of .
- Build the road between cities and at a cost of .
- Build the road between cities and at a cost of .
This gives a total cost of . Note that the road between cities and does not need to be built because each is connected to city .
In this scenario it is optimal to build a library in each city because the cost to build a library is less than the cost to build a road.

There are cities, so the total cost is .